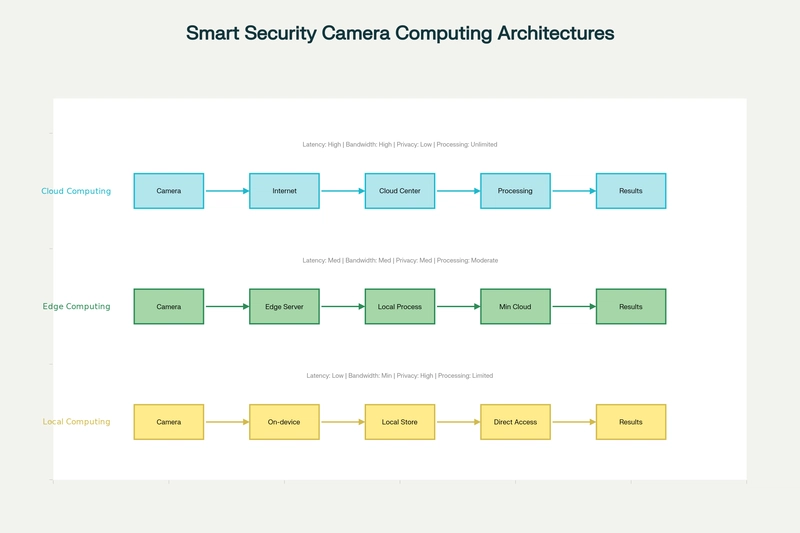
The way smart security cameras process data—cloud, edge, or local—can make or break your security system’s performance, cost, and privacy. Each approach has its perks and trade-offs, so picking the right one is crucial.
Cloud Computing
In cloud-based systems, cameras stream footage to remote servers for processing and storage. Platforms like AWS or Google Cloud offer massive computing power and advanced AI analytics for facial recognition, behavior tracking, and threat detection.
Advantages:
- Massive scalability and processing power
- Automatic updates and professional maintenance
- Redundant storage for high availability
Challenges:
- Latency can reach 100–500 milliseconds
- Continuous streaming consumes bandwidth
- Sensitive data is transmitted to third-party servers, raising privacy concerns
Edge Computing
Edge computing bridges the gap between cloud and local processing by analyzing data close to its source. Cameras or local servers handle initial analysis, sending only relevant insights to the cloud.
Benefits:
- Reduced latency (10–50 milliseconds)
- Lower bandwidth usage
- Reliable operation even with intermittent internet
Examples:
Systems like VORTEX or EnGenius AI Cloud Edge Cameras provide real-time threat detection, human recognition, and loitering alerts locally before syncing with the cloud.
Local Processing
Local systems keep all data on-site, leveraging AI-enabled cameras or dedicated servers.
Advantages:
- Ultra-low latency (1–10 milliseconds)
- Maximum privacy and data control
- Fully operational without internet
Limitations:
- High initial hardware costs
- Maintenance and updates must be handled internally
- Scaling requires physical hardware upgrades
Choosing the Right Approach
A hybrid strategy is increasingly popular—local analysis for immediate threats, edge processing for sophisticated detection, and cloud storage for long-term archiving. Advances in edge AI and 5G make balancing speed, security, and cost more efficient than ever.
Ultimately, the best architecture depends on your latency needs, bandwidth limits, privacy requirements, and budget. Evaluate your environment carefully to ensure your smart security cameras deliver peak performance without compromise.