In this tutorial, we will demonstrate:
- Cursor: Processing rows with a condition.
- Trigger: Automatically inserting audit logs after an insert operation.
We’ll use simple examples with screenshots from an online MySQL editor.
Cursor Example: Employees with Salary > 50,000
Step 1: Create Employee table & Insert sample data
CREATE TABLE Employee (
emp_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
emp_name VARCHAR(50),
salary INT
);
INSERT INTO Employee VALUES
(1, 'Alice', 40000),
(2, 'Bob', 55000),
(3, 'Charlie', 70000),
(4, 'David', 45000);
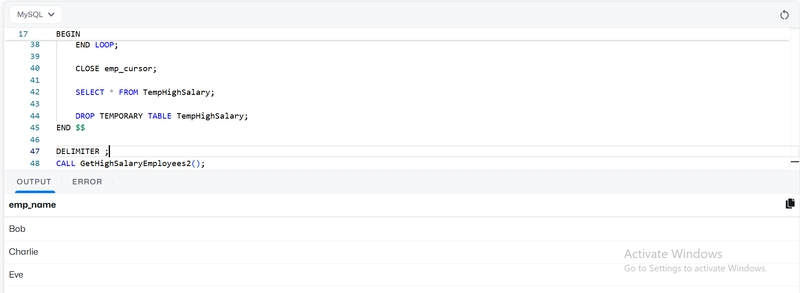
Step 2: Use a Cursor with Condition
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE GetHighSalaryEmployees()
BEGIN
DECLARE done INT DEFAULT FALSE;
DECLARE empName VARCHAR(50);
DECLARE cur CURSOR FOR SELECT emp_name FROM Employee WHERE salary > 50000;
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR NOT FOUND SET done = TRUE;
OPEN cur;
read_loop: LOOP
FETCH cur INTO empName;
IF done THEN
LEAVE read_loop;
END IF;
SELECT empName AS High_Salary_Employee;
END LOOP;
CLOSE cur;
END//
DELIMITER ;
Step 3: Call the Procedure
CALL GetHighSalaryEmployees();
Trigger Example: Student Registration Audit
Step 1: Create Student & Audit tables
CREATE TABLE Students (
student_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50)
);
CREATE TABLE Student_Audit (
audit_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
student_id INT,
name VARCHAR(50),
registered_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
Step 2: Create AFTER INSERT Trigger
DELIMITER //
CREATE TRIGGER after_student_insert
AFTER INSERT ON Students
FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
INSERT INTO Student_Audit (student_id, name)
VALUES (NEW.student_id, NEW.name);
END //
DELIMITER ;
Step 3: Insert Data into Students
INSERT INTO Students VALUES (1, 'John Doe');
INSERT INTO Students VALUES (2, 'Jane Smith');
Step 4: Check Audit Table
SELECT * FROM Student_Audit;
CONCLUSION
- Cursor helps process row-by-row results under certain conditions.
- Trigger automates actions (like auditing) whenever an event occurs in a table.
Both are powerful features in SQL for automation and data integrity.