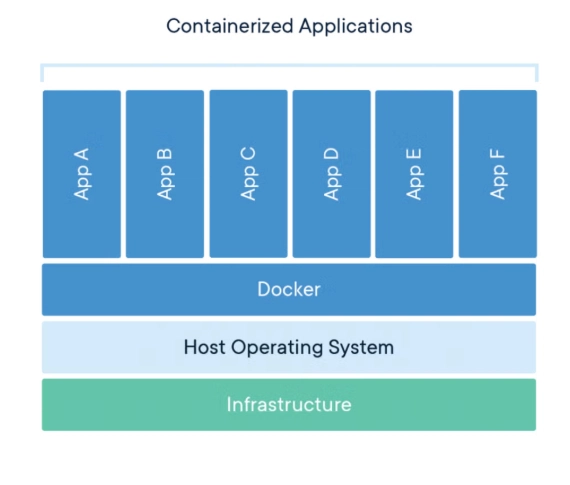
What is Docker
Docker is an open source platform that enables developers and engineers to build, deploy, run and manage containers.
Containers are standardized, executable components that combine application source code, together with the operating System libraries and dependencies required to run that code in any environment.
containers enable multiple application components to share the resources of a single instance of the host Operating System.
Why use Docker
- Consistency: Docker deals with the infamous headache of “It works on my machine” problem. This problem occurs when an application works on the developers laptop, but when the application is deployed in to a server or the cloud, something breaks. Docker helps to package everything the app need into a container Image. That container image will run the same way on any machine (laptop, staging server, production in cloud).
-
Light Weight: Docker containers share the Host OS kernel. they don’t need to boot an entire OS each time like is the case with traditional Virtual Machines. As a result:
-Containers start quickly.
-Save cost on hardware and cloud resources.
-You can run many containers on a single machine. - Scalable: With docker you can run multiple containers of the same app behind a load balancer. You can add more containers (Scale up) when demand increases of remove container (scale down) when demand decreases.
- Fast Deployment: With docker, you build an image and to starting a new container is an automated and repeatable process.
Terms and Tools within docker Architecture
- Docker Host:- This is the physical or virtual machine running a Docker engine compatible Operating System such as the Linux.
- Docker Engine:’- It a client/server application that consist of the Docker Daemon, Docker API that interacts with the Daemon, and a Docker CLI that talks to the daemon.
- Docker Daemon:- This is a service that creates and manages docker images by using commands from the client.
- Docker client:-Provides the Command Line Interface (CLI) that accesses the Docker API to communicate with the Docker Daemon over a unix socket or a network interface.
- Docker Object:- components of a docker deployment that help package and distribute applications. They include Images, containers, network, plugins, and volumes.
- Container:- This is the live running instance of a docker Image.
- Docker Image:- Contain executable applications source code and all tools, libraries and dependencies the application code needs to run as a container.
- Docker Build:- a command that has tools and features for creating a docker image.
- Docker file:- A simple text file containing instructions for how to build the docker container image. You can say it is a list of instructions that the docker engine will run to assemble the docker image.
-
Docker Hub this is a public repository of docker images.
11 Docker Compose: is a tool to manage multiple container applications where all containers run on the same docker host.
Docker Installation
sudo apt update
sudo apt install docker.io -y
sudo systemctl enable docker --now
Verify Installation
docker version
Running your first container
docker run hello-world
👆Docker pulls the image from Docker Hub and runs it inside a container
Basic docker commands
# Pull an image from Docker Hub
docker pull ubuntu
# Run a container
docker run -it ubuntu bash
# List running containers
docker ps
# List all containers (including stopped)
docker ps -a
# Stop a container
docker stop
# Remove a container
docker rm
# Remove an image
docker rmi
Building an Image
create a file called Dockerfile:
# Use Python base image
FROM python:3.9-slim
# Set working directory
WORKDIR /app
# Copy files
COPY . /app
# Install dependencies
RUN pip install flask
# Run the app
CMD ["python", "app.py"]
Build and run
docker build -t myapp .
docker run -p 5000:5000 myapp
Managing Multi-Container Applications using Docker-compose
In real projects , applications often need multiple services working together. For example:
- A web application (Flask, Django or Node.js)
- A database (PostgreSQL, MongoDB)
- Cache (Reds)
Running and connecting each container manually with docker run can get messy.
## Why use docker compose
We use docker compose to define and manage multi-container applications using a single YAML file (docker-compose.yml)
To run docker compose, just run:
docker-compose up
Sample Docker Compose File
Here is a simple example: a Flask app with a PostgreSQL database.
version: '3.8'
services:
web:
build: .
ports:
- "5000:5000"
depends_on:
- db
db:
image: postgres:13
environment:
POSTGRES_USER: myuser
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: mypassword
POSTGRES_DB: mydb
ports:
- "5432:5432"
How it works
- Web -> Your Flask app (built from the dockerfile in the current directory).
- db -> A PostgreSQL database running in its own container.
- depends_on -> Ensures the database starts befor the web app
Running docker composedocker-compose up
👆This launches both containers (web + db)
To Stop them, run:docker-compose down
Why docker compose is useful
- Simplifies running multiple containers.
- Keeps your setup reproducible and sharable.
- Handles networking automatically (services can talk to each other by names, e.g., db)