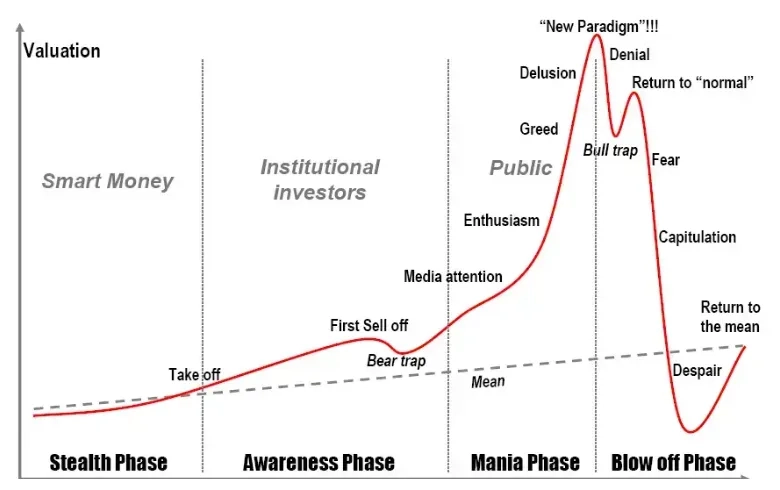
It is a significant decline in economic activity that lasts for a period of time — typically two or more consecutive quarters (6 months) — across the economy.
- Decline in GDP (Gross Domestic Product)
- Rising unemployment
- Drop in consumer spending
- Reduced business investments
- Lower industrial production
Ex. Imagine a country where:
- Companies are making fewer products
- People are losing jobs
- Shops are seeing fewer customers
- Everyone is spending less money
Reason: To control inflation (when prices are rising too fast)
Example:
Let’s say prices of groceries, fuel, and goods are going up rapidly in India (i.e., high inflation).
- RBI increases repo rate from 6% → 6.5%
- Now banks have to pay more interest to borrow from RBI
- So banks increase loan interest rates for people and businesses
- Result: Less borrowing, less spending
- Demand drops → Prices come down → Inflation is controlled
Reason: To boost economic growth (especially during slowdowns or recession)
Example:
During COVID-19, businesses were down, jobs were lost, and people stopped spending.
- RBI cuts repo rate from 6% → 4%
- Banks can now borrow cheaply
- They lower interest rates on home loans, car loans, business loans
- More people and businesses start borrowing and spending
- Demand rises → Businesses grow → Economy recovers
Stay Connected!
If you enjoyed this post, don’t forget to follow me on social media for more updates and insights:
Twitter: madhavganesan
Instagram: madhavganesan
LinkedIn: madhavganesan