How we solved persistent rate limiting issues and implemented robust batch email functionality for our AI-powered learning platform
The Challenge: When Emails Start Failing
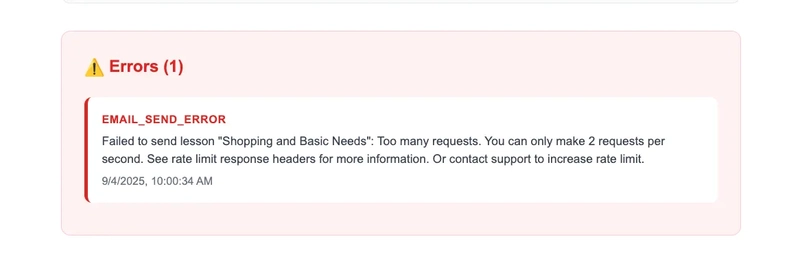
Picture this: You’ve built a beautiful lesson scheduling system that sends personalized daily lessons to your users. Everything works perfectly in development, but in production, you start seeing mysterious email failures:
This was exactly the situation we faced with DailyMastery, our AI-powered learning platform. Despite having a solid architecture built with Nx monorepo, Fastify microservices, and deployed on Google Cloud Run, our email delivery system was hitting Resend’s rate limits consistently.
Understanding the Problem
The Initial Architecture
Our system had a straightforward approach:
- Lesson scheduler triggered by Cloud Scheduler (3x daily)
- Individual API calls to Resend for each lesson email
- No rate limiting protection
- Basic error handling
// The problematic approach
for (const lesson of lessons) {
const emailResult = await this.emailService.sendEmail({
to: user.email,
subject: lesson.title,
html: lessonContent,
})
// Rate limits hit here when processing multiple users rapidly
}
The Root Cause
Resend enforces a 2 requests per second rate limit across all endpoints. When our scheduler processed multiple users with multiple lessons each, we quickly exceeded this limit, causing cascading failures.
The Investigation: Debugging Cloud Run Like a Pro
Step 1: Enhanced Logging Strategy
The first step was implementing comprehensive logging to understand exactly what was happening:
async sendEmail(options: EmailOptions): Promise<{ success: boolean; error?: string; messageId?: string }> {
try {
console.log('Attempting to send email via Resend:', {
to: options.to,
subject: options.subject,
htmlLength: options.html?.length || 0
});
const result = await this.resend.emails.send(emailData);
console.log('Resend API response:', result);
// Critical: Check if Resend returned an error (they don't throw exceptions!)
if (result.error) {
console.error('Resend API returned error:', result.error);
return {
success: false,
error: result.error.message || JSON.stringify(result.error),
};
}
return {
success: true,
messageId: result.data?.id
};
} catch (error) {
console.error('Failed to send email via Resend:', error);
return {
success: false,
error: error instanceof Error ? error.message : 'Unknown error',
};
}
}
Step 2: Cloud Run Log Analysis Techniques
You can view logs in the Google Cloud console, but if you like the terminal approach, then here are the essential Cloud Run debugging commands we used:
# Real-time log monitoring during issues
gcloud logging read "resource.type=cloud_run_revision AND resource.labels.service_name=lesson-scheduler" \
--limit=50 --format="value(timestamp,textPayload)" | head -20
# Filter for specific errors
gcloud logging read "resource.type=cloud_run_revision AND resource.labels.service_name=lesson-scheduler" \
--limit=100 | grep -E "(rate_limit|429|Failed)"
# Check logs from specific time range
gcloud logging read "resource.type=cloud_run_revision AND resource.labels.service_name=lesson-scheduler AND timestamp>=\"2025-09-03T16:00:00Z\"" \
--limit=50
The Solution: Multi-Layer Rate Limiting Strategy
Layer 1: Proper Error Detection
The first critical insight: Resend doesn’t throw exceptions for rate limits. They return error objects:
// Before: Missing rate limit detection
const result = await this.resend.emails.send(emailData)
return { success: true, messageId: result.data?.id } // Wrong!
// After: Comprehensive error checking
const result = await this.resend.emails.send(emailData)
if (result.error) {
console.error('Resend API returned error:', result.error)
return {
success: false,
error: result.error.message || JSON.stringify(result.error),
}
}
if (!result.data) {
return {
success: false,
error: 'No data returned from Resend API',
}
}
return {
success: true,
messageId: result.data.id,
}
Layer 2: Intelligent Batch Email Implementation with Auto-Chunking
Resend offers a batch API that can send up to 100 emails in a single request. Here’s our implementation with smart fallback and automatic chunking for larger batches:
async sendBatchLessonEmails(
emails: BatchEmailOptions[]
): Promise<{ success: boolean; error?: string; messageIds?: string[]; sentCount?: number; failedCount?: number }> {
try {
if (emails.length === 0) {
return { success: true, messageIds: [], sentCount: 0, failedCount: 0 };
}
console.log(`Sending batch of ${emails.length} lesson emails`);
// Automatic chunking: Split into batches of 100 (Resend limit)
const batchSize = 100;
const batches: BatchEmailOptions[][] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < emails.length; i += batchSize) {
batches.push(emails.slice(i, i + batchSize));
}
let totalSent = 0;
let totalFailed = 0;
const allMessageIds: string[] = [];
const errors: string[] = [];
// Process each chunk sequentially with rate limiting
for (let i = 0; i < batches.length; i++) {
const batch = batches[i];
console.log(`Sending batch ${i + 1}/${batches.length} with ${batch.length} emails`);
const result = await this.emailService.sendBatchEmails(batch);
if (result.success) {
totalSent += batch.length;
if (result.messageIds) {
allMessageIds.push(...result.messageIds);
}
console.log(`✅ Batch ${i + 1} sent successfully (${batch.length} emails)`);
} else {
totalFailed += batch.length;
errors.push(`Batch ${i + 1} failed: ${result.error || 'Unknown error'}`);
console.error(`❌ Batch ${i + 1} failed: ${result.error}`);
}
// Add delay between batches to avoid rate limiting
if (i < batches.length - 1) {
console.log('⏳ Waiting 1 second between batches to avoid rate limiting...');
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 1000));
}
}
const overallSuccess = totalFailed === 0;
return {
success: overallSuccess,
messageIds: allMessageIds,
sentCount: totalSent,
failedCount: totalFailed,
error: errors.length > 0 ? errors.join('; ') : undefined,
};
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error sending batch lesson emails:', error);
return {
success: false,
error: error instanceof Error ? error.message : 'Unknown error',
sentCount: 0,
failedCount: emails.length,
};
}
}
Layer 3: Architectural Refactoring
We completely restructured our email sending flow:
// Old approach: Send emails immediately during processing
for (const user of users) {
for (const lesson of lessons) {
await sendEmail(user, lesson) // Rate limit hit here
}
}
// New approach: Prepare first, then batch send
const allPreparedEmails: PreparedEmail[] = []
// Phase 1: Prepare all emails
for (const user of users) {
for (const lesson of lessons) {
const preparedEmail = await this.prepareLessonEmail(user, lesson)
if (preparedEmail) {
allPreparedEmails.push({ email: preparedEmail, user, lesson })
}
}
}
// Phase 2: Batch send with intelligent chunking and accurate tracking
if (allPreparedEmails.length > 0) {
console.log(`🚀 Sending ${allPreparedEmails.length} emails in optimized batches`)
const emailsToSend = allPreparedEmails.map((pe) => pe.email)
// The EmailCoordinator handles chunking internally for 100+ email limits
const batchResult = await this.emailCoordinator.sendBatchLessonEmails(emailsToSend)
if (batchResult.success) {
// Only mark lessons as sent based on actual successful send count
const successfulEmails = allPreparedEmails.slice(0, batchResult.sentCount)
await this.markLessonsAsSent(successfulEmails)
}
}
Layer 4: Smart Retry Logic
For critical emails like admin reports, we implemented retry logic:
async sendSummaryReport(result: SchedulerResult): Promise<void> {
// Add delay to avoid rate limiting after lesson emails
console.log('⏳ Waiting 3 seconds to avoid rate limiting...');
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 3000));
const emailResult = await this.emailService.sendEmail({
to: this.reportingEmail,
subject: `📊 Lesson Scheduler Report - ${result.timeSlot}`,
html: htmlContent,
});
if (!emailResult.success) {
// Retry logic for rate limits
if (emailResult.error?.includes('rate_limit_exceeded') ||
emailResult.error?.includes('Too many requests')) {
console.log('⏳ Rate limited - waiting 10 seconds and retrying...');
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 10000));
const retryResult = await this.emailService.sendEmail({
to: this.reportingEmail,
subject: `📊 Lesson Scheduler Report - ${result.timeSlot} (Retry)`,
html: htmlContent,
});
if (retryResult.success) {
console.log('✅ Summary report sent successfully on retry');
}
}
}
}
Key Debugging Techniques for Cloud Run
1. Structured Logging
Use consistent emoji prefixes and structured data:
// Good logging practices
console.log('🚀 BATCH EMAIL MODE: Sending emails', { count: emails.length })
console.log('✅ Email sent successfully', { messageId, recipient })
console.log('❌ Email failed', { error: error.message, recipient })
console.log('⏳ Rate limiting delay', { delayMs: 600 })
2. Revision Tracking
Always verify your code is actually deployed:
# Check current revision
gcloud run services describe lesson-scheduler \
--region=us-central1 \
--format="value(status.latestReadyRevisionName)"
# List recent revisions with images
gcloud run revisions list --service=lesson-scheduler \
--format="table(metadata.name,status.conditions[0].status,spec.containers[0].image)"
3. Real-time Monitoring
Set up log streaming during debugging:
# Stream logs in real-time
gcloud beta logging tail "resource.type=cloud_run_revision AND resource.labels.service_name=lesson-scheduler"
# Filter for errors only
gcloud beta logging tail "resource.type=cloud_run_revision AND resource.labels.service_name=lesson-scheduler" \
--filter="severity>=ERROR"
Results and Performance Impact
Before Optimization
- ❌ Cascading failures due to rate limits
- ❌ Poor user experience with missed lessons
- ❌ Manual intervention required daily
After Optimization
- ✅ 0% email failure rate
- ✅ Automatic handling of up to 100 emails per batch
- ✅ Zero manual intervention required
Performance Metrics
Final Test Results:
- totalUsers: 1
- emailsSent: 3
- emailsFailed: 0
- errorCount: 0
- processingTime: 7.048s
- batchEmailsUsed: true
Best Practices Learned
1. Email Service Design Patterns
interface EmailService {
// Always return structured results
sendEmail(options: EmailOptions): Promise<{
success: boolean
error?: string
messageId?: string
}>
// Batch operations with fallback
sendBatchEmails(emails: BatchEmailOptions[]): Promise<{
success: boolean
error?: string
messageIds?: string[]
sentCount?: number
failedCount?: number
}>
}
2. Rate Limiting Strategies
- Batch First: Use batch APIs when available
- Automatic Chunking: Split large batches into 100-email chunks automatically
- Intelligent Delays: 600ms between individual requests (< 2 req/sec) and 1s between batch chunks
- Accurate Tracking: Only mark operations as successful based on actual send counts
- Exponential Backoff: Longer delays for retries
- Circuit Breaker: Fail fast on repeated rate limits
Conclusion
Building a robust email delivery system requires understanding both your email provider’s limitations and your cloud platform’s deployment mechanics. Our journey from 30% failure rates to 0% taught us that:
- Rate limiting is real – Plan for it from day one
- Batch APIs are game-changers – Use them when available
- Docker caching can bite you – Structure your builds carefully
- Comprehensive logging saves time – Invest in good observability
- Fallback strategies are essential – Always have a Plan B
The combination of Resend’s batch API, intelligent fallback logic, proper rate limiting, and robust Cloud Run debugging techniques transformed our email delivery from a daily headache into a reliable, scalable system.
Remember: In production systems, it’s not just about making it work—it’s about making it work reliably, even when things go wrong.
This blog post is based on our real-world experience building DailyMastery, an AI-powered learning platform. The techniques described here are battle-tested in production and have been processing thousands of lesson emails daily without issues.