AWS Lambda is a serverless technology that lets you deploy your application without having to deploy servers. You essentially deploy tour code, configure basic settings like memory, ephemeral storage and IAM role and that’s it, you are good to go.
What is Code Signing?
Code signing is a security process that applies a digital signature to software code or executables to prove the authenticity and integrity of your code. So, what does it mean?
You have deployed your code but how do you know the deployed code has not been tampered with? That’s the problem Code Signing solves.
- Authenticity: the code is deployed by a trusted source like yourself or your company.
- Integrity: the code has not been modified since it was signed.
- Non-repudiation: the signer like you cannot later deny having signed it.
What is AWS Signer?
AWS Signer is a fully managed code signing service from AWS.
It lets you digitally sign your software, deployment packages, and container images so that AWS services like Lambda or IoT can verify the code’s integrity and authenticity before running it.
You can also use AWS Signer from CI/CD pipeline which is critical given most companies deploy code using CI/CD. This helps us confirm that only authorized, untampered code gets deployed.
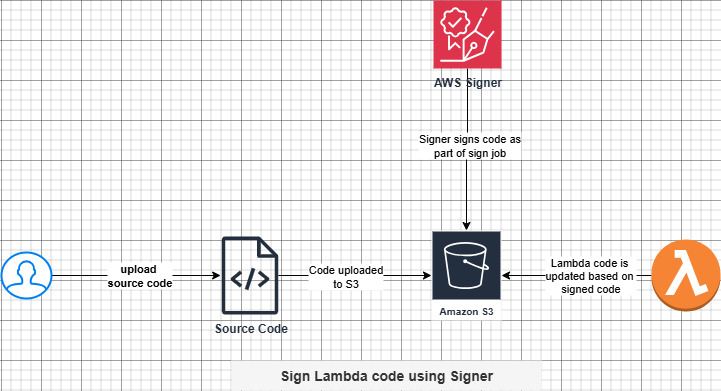
How Signer Signs Lambda Code
To use AWS Signer, you need to create a signing profile as shown below.
To use AWS Signer, you need to upload the code to a S3 bucket. You can setup the bucket so that the signed and unsigned code are kept in different prefix. Once code is uploaded, you can run a sign job from AWS Signer. This will produce the signed code in the S3 bucket. After that, you can update the Lambda code with the signed code.
You also need to update signing profile setting in Lambda. Under Lambda dashboard, you can set the default configuration for signing. This is shown below.
You can choose one or more signing profiles. Note the Signature validation policy. You can set it to Warn or Enforce. For experimentation, you can start with Warn and eventually change it to Enforce. Once you enforce it, Lambda blocks the deployment request if the signature validation check fails. This ensures that only trusted and signed code is deployed to Lambda functions, providing a stricter security posture.
How to use Signing Profile in Lambda Function
Now, all the settings are done, you just need to start using the signing profile in your Lambda function. To do that, when you create a new Lambda function from console, you need to expand Additional configurations and select Code Signing under Security & governance. This is shown below.
Update Lambda Function to with Signed Code
Ok, we have the signing profiles ready. Now, we need to sign the code. So, as I mentioned before,
- Upload code to a S3 bucket
- Create a signing job from AWS Signer and choose the right signing profile
- Update Lambda function to use the signed code
Note, once you have used signed code in Lambda, you can no longer view the code in AWS Lambda console. You can check the signing profile under Code properties in Lambda.
What Happens When a Signing Certificate Expires
Signer-managed certificates have a validity period that you can set. When a signing certificate expires:
- Existing signed artifacts remain valid (they include timestamp metadata proving they were signed during a valid period).
- You cannot sign new artifacts using the expired certificate.
- You must create a new signing profile and sign again.
This is important for AWS Lambda code signing, since Lambda will reject expired signatures at deployment time.
Conclusion
To wrap up, AWS Lambda code signing brings cryptographic assurance to serverless deployments, ensuring that only verified, untampered code runs in your functions. It’s a small implementation effort with a big payoff in security and trust.